Within the portfolio of energy storage technologies, hydrogen is widely recognized as a promising option for storing large quantities of renewable electricity over longer periods.
Additionally, it is predicted to also be the energy vector for a more sustainable mobility and a renewable feedstock for a variety of chemical productions, potentially becoming a central pillar for promoting energy transition to sustainable sources and world economy decarbonization.
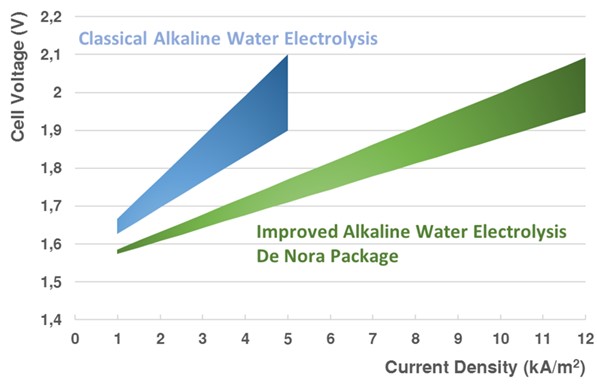
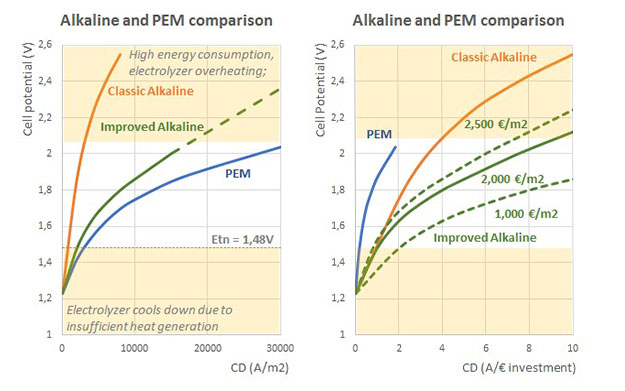
The most established technology option for producing hydrogen from electrical power sources is water electrolysis (WE). With a 100% renewable energy power mix, water electrolysis can produce GREEN HYDROGEN with zero CO2 emissions.